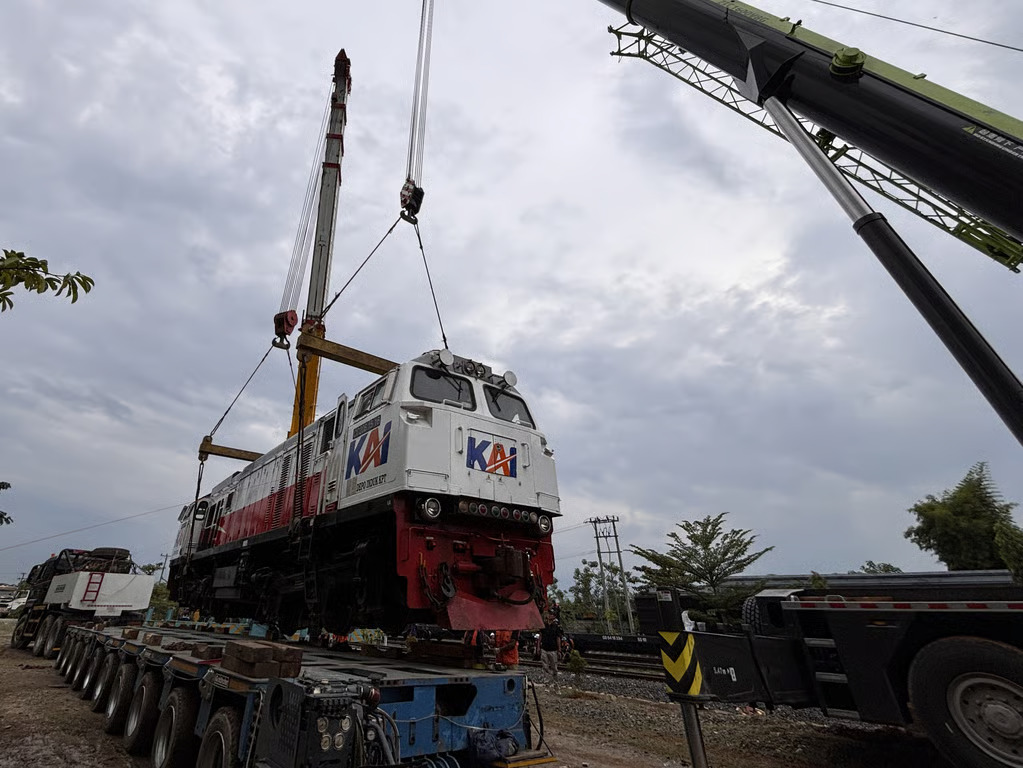
Social entrepreneurship in Singapore has become a vital tool for addressing the city-state’s most pressing social and environmental challenges. These businesses, founded on a mission to create positive change, operate with a dual purpose: to achieve financial success and to address critical issues in society. As Singapore continues to promote social entrepreneurship, the country has become a model for integrating social impact into business practices.
A major factor contributing to the success of social entrepreneurship in Singapore is the strong support from the government. Initiatives like the National Social Entrepreneurship Foundation and various funding programs have provided financial assistance and resources for social enterprises. These policies are designed to help businesses scale and reach more communities, thereby amplifying their positive impact.
The social entrepreneurship landscape in Singapore is diverse, encompassing businesses that focus on education, healthcare, sustainability, and social inclusion. For instance, Makan Kaki, a social enterprise, connects migrant workers with local food vendors, creating a platform that empowers migrant workers to access affordable and nutritious meals. This initiative not only addresses the issue of food insecurity but also supports the livelihoods of local vendors.
Singaporean social enterprises are also tackling the challenge of environmental sustainability. The Green Collective, a community-driven platform that promotes sustainable living, connects consumers with eco-friendly products and services. Through its work, the enterprise encourages individuals and businesses to make more environmentally conscious choices, helping to reduce waste and conserve resources.
Another area where social entrepreneurship in Singapore has made an impact is in education. TFA, The Future Academy, provides scholarships, mentorship programs, and training to underserved students, helping them gain access to higher education and career opportunities. By focusing on education, TFA is addressing inequality and empowering young individuals to succeed in a competitive world.
The model of social enterprises in Singapore is often based on the idea of self-sustainability, where profits generated from business operations are reinvested into the social mission. This creates a model where businesses are not only generating revenue but also contributing to the well-being of society. This approach has attracted investors who are increasingly interested in supporting ventures that create tangible social benefits.
Social enterprises in Singapore are changing the narrative of what it means to be a successful business. They are demonstrating that businesses can thrive while addressing societal issues such as inequality, mental health, and environmental sustainability. With continued support from the government and private sector, Singapore’s social enterprises will continue to evolve and create lasting positive impacts on both local and global communities.